Сварка плавлением является наиболее универсальным способом соединения деталей, применяемых в изготовлении изделий во всех областях промышленности. Волоконный лазер это современный и надежный концентрированный источник тепла.
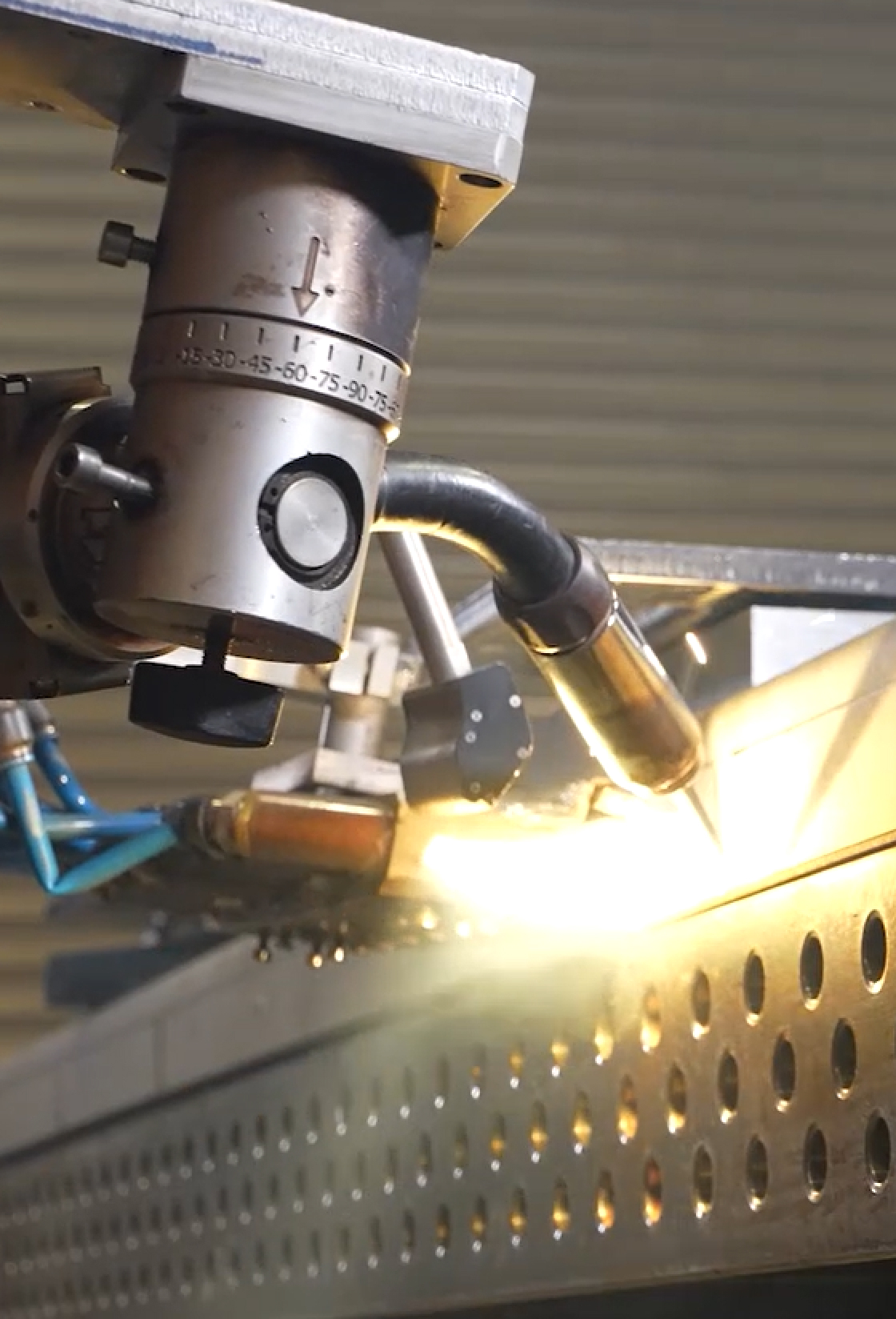
Лазерная сварка осуществляется сконцентрированным лазерным лучом, который имеет высокую плотность мощности (более 1МВт/см2), при этом размер фокусного пятна варьируется от 0,1 до 1 мм. Это дает возможность осуществлять сварку с глубоким проплавлением пропорционально количеству вкладываемой энергии (от 0,1 до 30 мм). При этом скорость сварки обычно превышает в несколько раз скорость сварки дуговой и плазменной сварки.
Лазерная сварка является универсальным процессом, способным сваривать углеродистые, низколегированные, высокопрочные, нержавеющие стали, сплавы алюминия и титана, пластмассы, а также различные разнородные материалы. Сварка обычно осуществляется в защитной газовой среде: аргона (Ar), гелия (He) и иногда азоте (N2), или различных смесей газов.
Качество сварных соединений выполненных лазерной сваркой является высоким и близким по своим физико-механическим свойствам основного материала. Лазерная сварка легко встраивается в производственные линии и может быть полностью автоматизирована.
Существуют различные виды лазерных сварных соединений: стыковой, внахлест, тавровый, торцевой, угловой. Обычно лазерная сварка осуществляется без разделки кромок за один проход.
При воздействии мощного сконцентрированного лазерного излучения на металл возникает эффект парогазового канала (keyhole). Считается, что парогазовый канал возникает под воздействием давления паров металла. Поглощение излучения в канале протекает не только за счет падения излучения на переднюю стенку канала, но и за счет плазменных процессов. Парогазовый канал является своеобразной оптической ловушкой для лазерного излучения, излучение в котором за счет переотражения движется как по оптическому кабель каналу проникая глубже в металл. Благодаря феномену парогазового канала сварной шов имеет «кинжальную» форму проплавления.
К преимуществам лазерной сварки относится:
- Высокая скорость сварки (1-10 м/мин).
- Сварка за один проход без разделки кромок («кинжальность» проплавления).
- Минимальные термические поводки изделия.
- Минимальная зона термического влияния.
- Возможность сварки широкого спектра материалов.
- Гибкость процесса.
- Возможность автоматизация.
- Экономия электроэнергии и присадки.
- Комфортные условия труда, чистота
Присутствуют также и недостатки:
- Повышенные требования к сборке.
- Жесткость термических циклов нагрева и охлаждения.
- Сложность подбора технологических режимов.
На сегодняшний день помимо обычной лазерной сварки различают другие виды лазерной сварки:
- гибридная сварка: с одновременным воздействием двух источников тепла: лазер+дуга, лазер+плазма; лазер+ТВЧ
- комбинированная: с последующим воздействием двух и более источников тепла: лазер и дуга, лазер и свет, лазер и плазма и т.д.
- «клещевая» сварка: замена контактной сварки
- «роллерная» сварка: осуществляется с одновременным поджимом роликом внахлест
- удаленная сварка: сварка на воздухе с расстояния более 1 м.
- многолучевая: использование двух и более лазерных источников в одной сварочной ванне.
- микросварка: сварка импульсными маломощными лазерами глубиной до 1 мм
Все эти виды лазерной сварки представляют широкие технологические возможности, благодаря которым конструктора могут создавать новые виды конструкций, которые ранее было изготовить крайне сложно или вовсе невозможно.